Wildfire
MONITORING, ASSESMENT AND REGENERATION
Sentinel-2 offers global, regular, and repeated coverage of terrestrial surfaces under cloud-free sky, which is ideal to map and monitor wildfires and their evolution over time by using the top-of-canopy surface reflectance. Based on these data, it is possible to develop systems to provide up-to-date and timeseries maps of Wildfires that can be used for monitoring purposes worldwide.
Wildfires affect thousands of people all over the world every year, destroy natural environments, and cause huge economic losses. The frequency and severity of these natural hazards are expected to increase as a consequence of climate change. It is therefore essential to develop monitoring tools to analyze the post-fire landscape evolution, to manage burnt areas, and to prevent the breakout of a fire in the future.
Sentinel-2 routinely collects large amounts of images which are made freely available. The vast amounts of data produced by the constellation of satellites are a great opportunity to develop systems for Wildfire Monitoring. To become fully operational, these processing systems must be entirely automatic with a controlled level of reliability and robustness.
See PDF

SENTINEL-2
Multispectral instrument (MSI)
13 spectral bands: four of them at 10 m spatial resolution
5 day revisit at equator

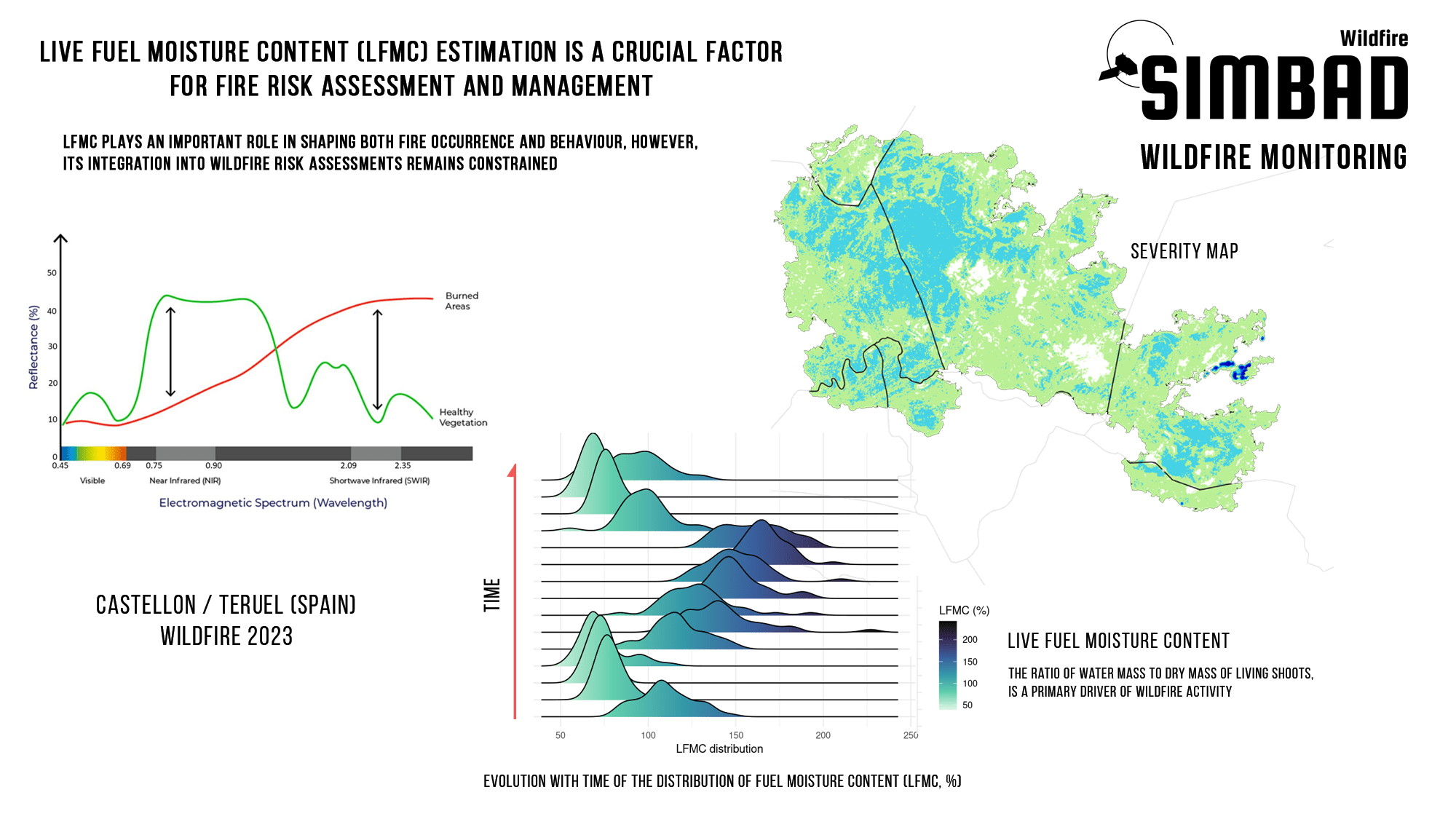
Remote sensing, particularly using satellites like Sentinel-2, plays a significant role in estimating the severity of wildfires. In pre-fire assessment, Sentinel-2 imagery can provide baseline data on vegetation health and land cover types before a wildfire occurs. This information serves as a reference for assessing post-fire changes. Sentinel-2 can detect active fires and map their extent in near real-time. By analyzing thermal bands and changes in vegetation indices, such as the Normalized Burn Ratio (NBR), analysts can identify areas affected by fire. After a wildfire, Sentinel-2 imagery is used to assess the extent and severity of the burn scar. Changes in vegetation health, soil properties, and the presence of ash and charred remains are visible in the imagery. One of the most common tools used, are Severity maps. Various indices derived from Sentinel-2 data, such as the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) or the Enhanced Vegetation Index (EVI), can quantify the severity of fire damage. Lower values indicate more severe damage, as vegetation is either burned or stressed. Last, Sentinel-2 can be used to monitoring the recovery rate of the burnt areas by comparing post-fire imagery with pre-fire conditions, analysts can track regrowth and ecosystem recovery over time.
Quasar can provide remote sensing tools to deal with the different stages associated with a wildfire, from prevention, to recovery.
Products | Applications | Services
Wildfire Monitoring Products
- S2 RGB and false color maps
- Wildfire burn severity maps
- External data enhancement maps
- Fire perimeter delineation
- Land use land cover (LULC) change maps
- Wildfire vulnerability maps
- Wildfire risk maps
- Recovery maps
Wildfire Monitoring Applications
The Wildfire Monitoring products can be used for different applications. Some example applications are:
- Categorization of burn severity levels applying spectral indices
- Delineation of the wildfire extent to support the decision-making process
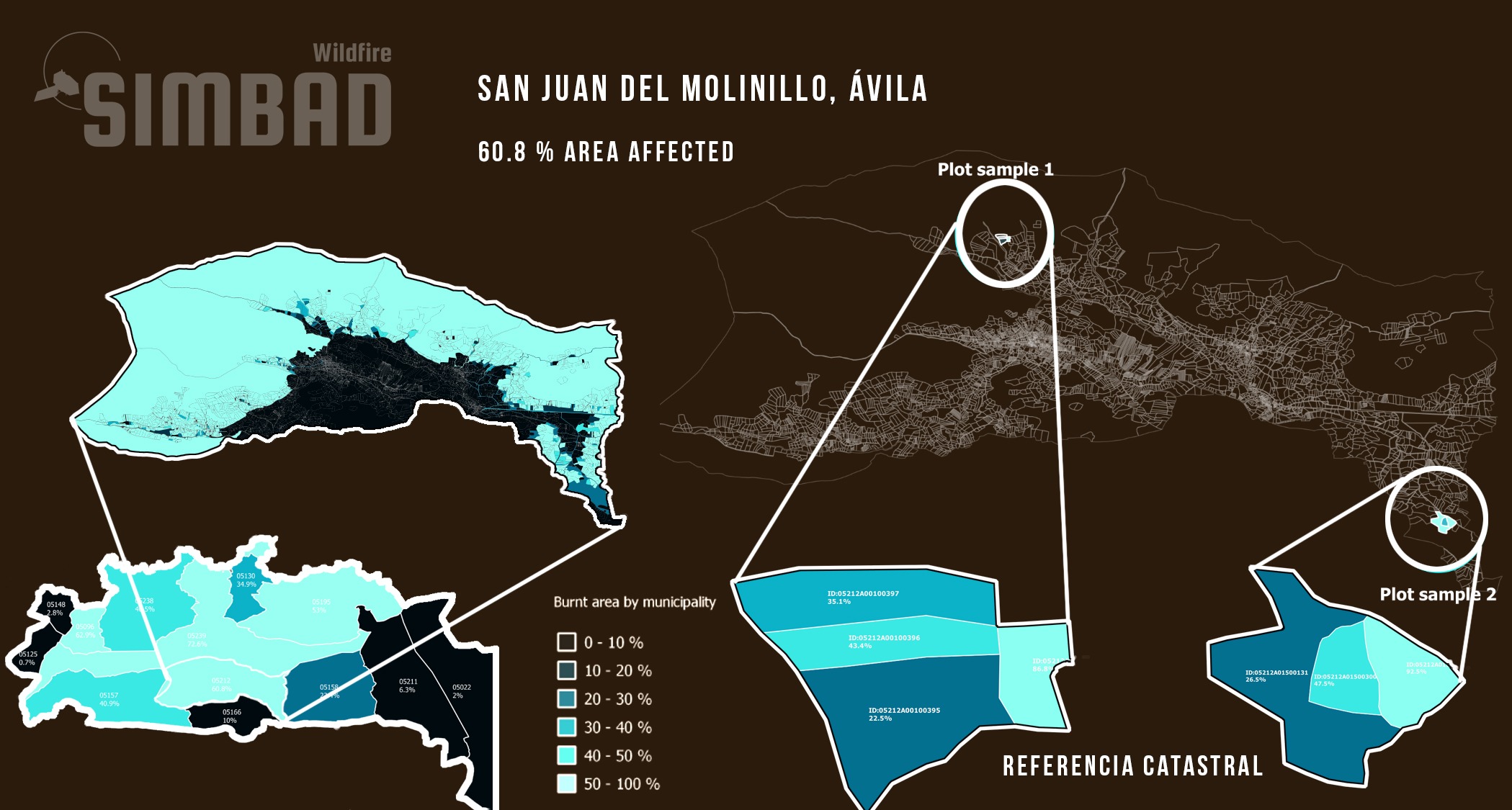
- Valuation of economic losses through the analysis of the impacted surfaces over different land designations (such as municipalities, plots, etc…)
- Environmental impact assessment after a wildfire-event (analysis of landslides, flooding, and erosion)
- Analysis of the vegetation cover evolution to asses and evaluate restoration plans
- Control land use changes after a wildfire-event
- Wildfire prevention, analysis of wildfire risk, exposure and vulnerability to avoid future wildfires in fire-prone areas
- Identification of priority forest restoration areas
- Prioritize wildfire surveillance and monitoring according to the level of risk areas
- Data-support for wildfire restoration plans
Wildfire Monitoring Services
- Dedicated tailor-made solutions for satellite and model-based Wildfire applications
- Transfer Wildfire analysis to diverse locations and Wildfire types
- Provide near real-time fire monitoring at a spatial resolution of 10 m
- Consulting services about Sentinel-2 data, products and applications
- Support the integration of Sentinel-2 data into your solution
- Support the integration of auxiliary non-EO data into your EO solution
- Support the integration of Copernicus Land Monitoring Service data into your solution
- Participation in R&D projects at national and European levels with experience leading projects and working within large collaborations
Wildfire Monitoring | Application Examples
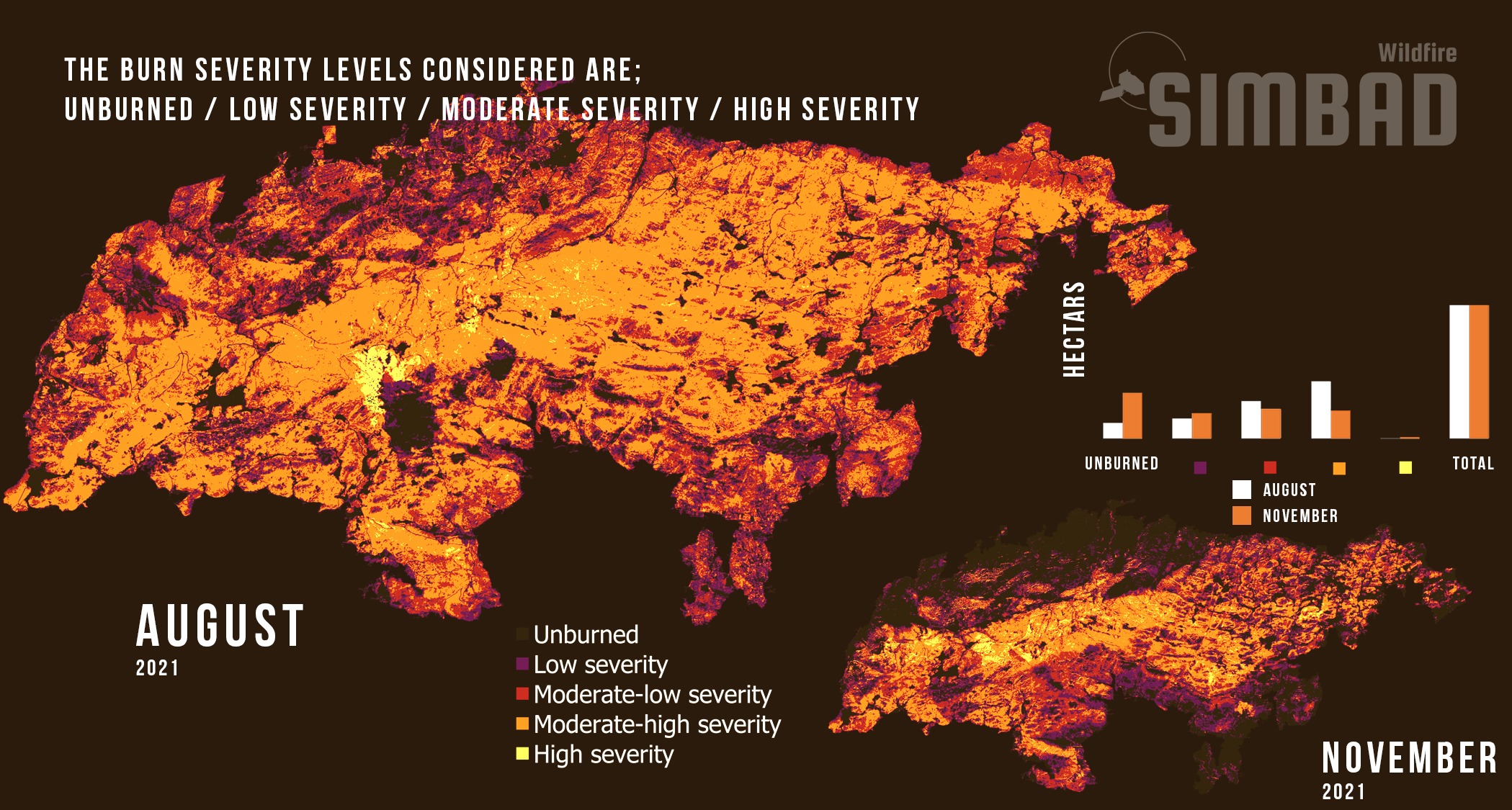
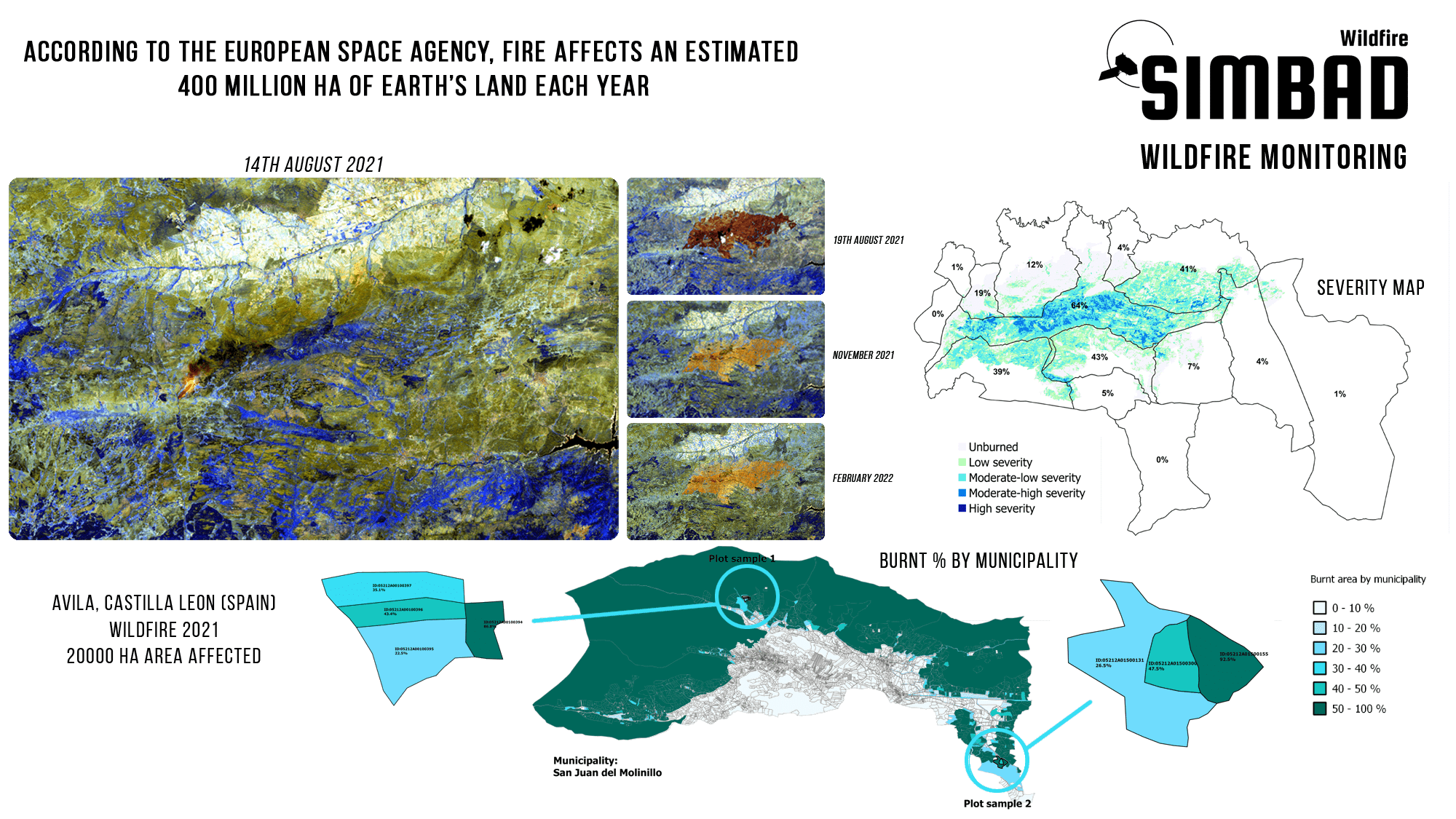
Wildfire Burnt Area
S2 imagery can be used to follow the recovery of affected burnt areas. In the case of the Ávila fire, the affected area were mostly occupied by forests and seminatural areas. Although Wildfires are common in Spain, this is the largest fire that Castilla and Leon has suffered in the last 40 years and the most serious of the year in the whole country.Wildfire Severity
After a Wildfire, it is crucial to assess the severity of the impacted area. The burnt severity is calculated through the comparison of pre-fire and post-fire S2 imagery. The temporal analysis of the burnt severity is paramount for the identification of priority forest restoration areas and the assessment of restoration measures.